One of the more common dental issues that you may face is gum disease. Gum disease is an infection of the gums that can advance to serious issues. For example, gum disease can cause tooth loss and bone deterioration. Typically, plaque will build along the gum line, irritating the soft tissues. However, there are several other reasons why you may develop gum disease.
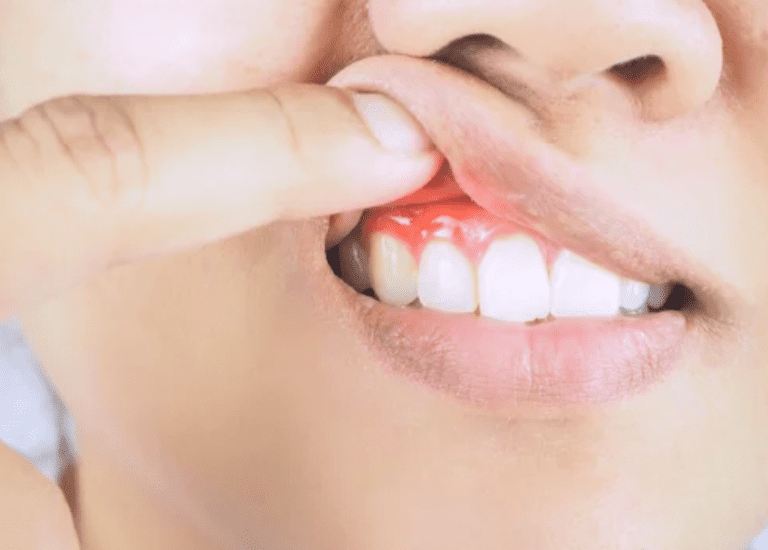
Poor Oral Hygiene
Poor oral hygiene is one of the most common causes of gum disease. When plaque and tartar build-up on the teeth and gums, it can irritate the soft tissues and lead to inflammation and infection. This is why brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing daily is crucial to gum health. Additionally, visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings is vital to your oral health.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Another major risk factor for gum disease is tobacco use. Tobacco use can cause inflammation and damage to the gums and reduce the immune system’s effectiveness in fighting off infections. Since gum disease is an infection, a diminished immune system increases your risk of gum disease. Quitting smoking or using tobacco products can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum disease.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or menopause, can also increase the risk of gum disease. Hormones can affect how the body responds to bacteria in the mouth, making it more susceptible to infection. If you are experiencing hormonal changes, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene habits and visit your dentist regularly.
Diabetes
Chronic medical conditions like diabetes can also increase the risk of gum disease. High blood sugar levels can lead to inflammation and damage to the blood vessels. This can impair the body’s ability to fight off infections like gum disease. If you have diabetes, it is important to maintain good blood sugar control and work closely with your healthcare provider to manage your condition.
Genetics
Sometimes, you have no control over developing gum disease. Genetics can also play a role in the development of gum disease. Some people may be more genetically susceptible to gum disease than others. If you have a family history of gum disease, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene habits and visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
Treatment Options
The treatment options for gum disease will depend on the severity of the condition. In the early stages of gum disease, known as gingivitis, treatment may involve a deep cleaning known as scaling and root planing. This involves removing plaque and tartar from the teeth and gums and smoothing the root surfaces to promote healing.
In more severe cases of gum disease, known as periodontitis, treatment may involve surgery to remove damaged tissue and restore the health of the gums. This may include procedures, such as gum grafting, bone grafting, and pocket reduction surgery.
